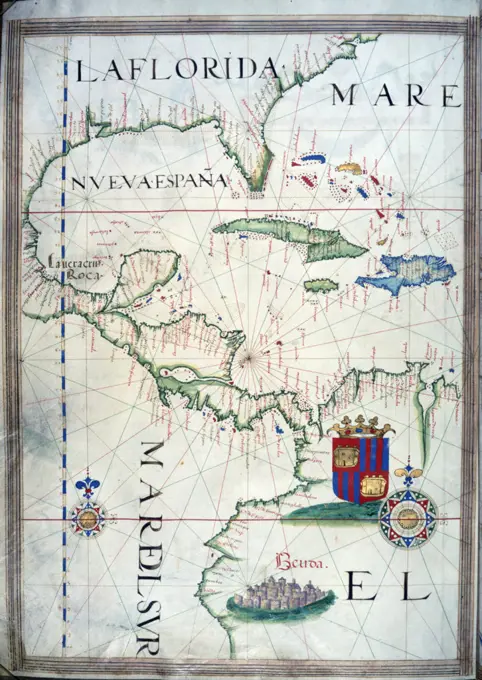
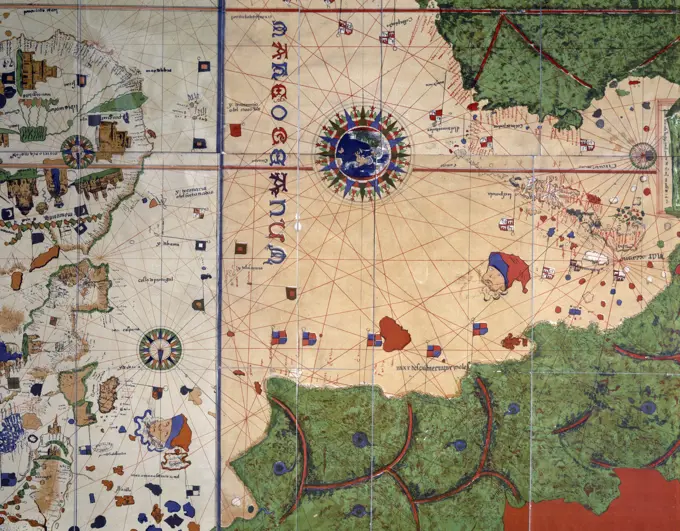
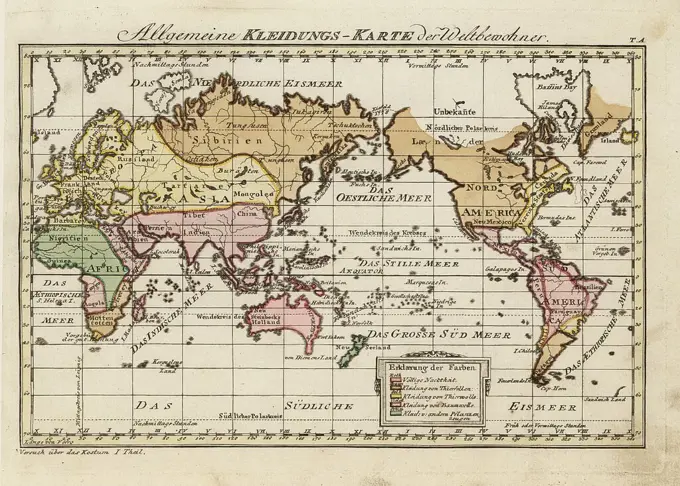
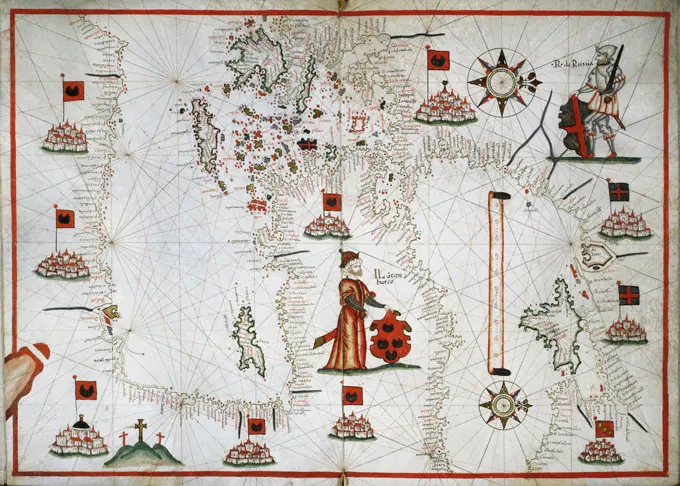
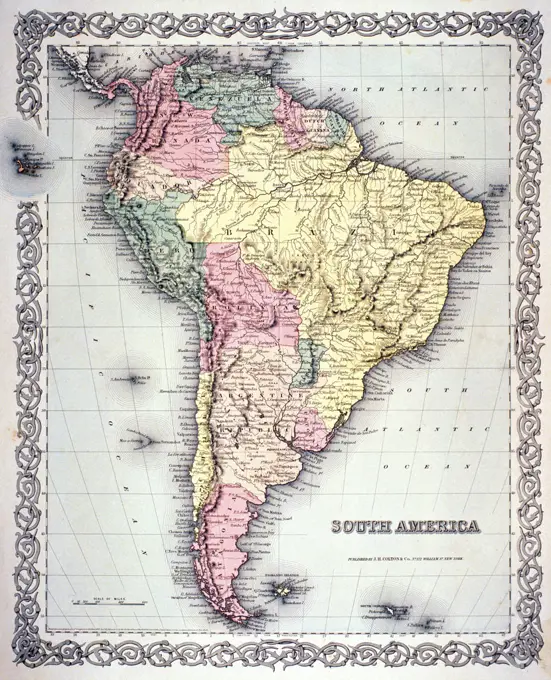
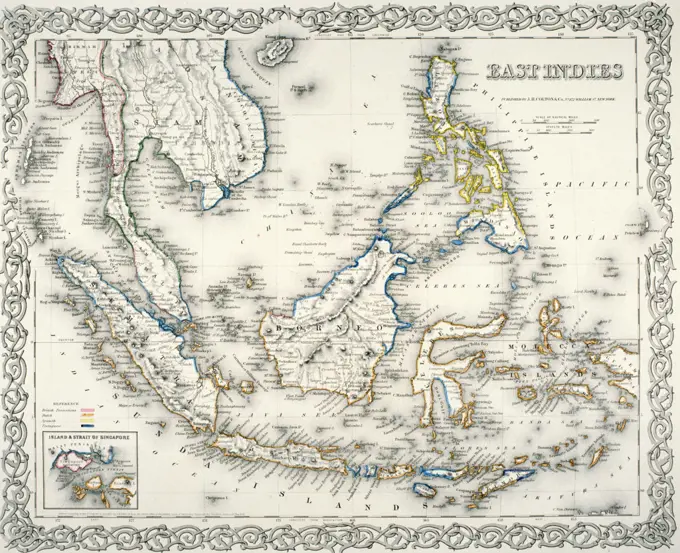
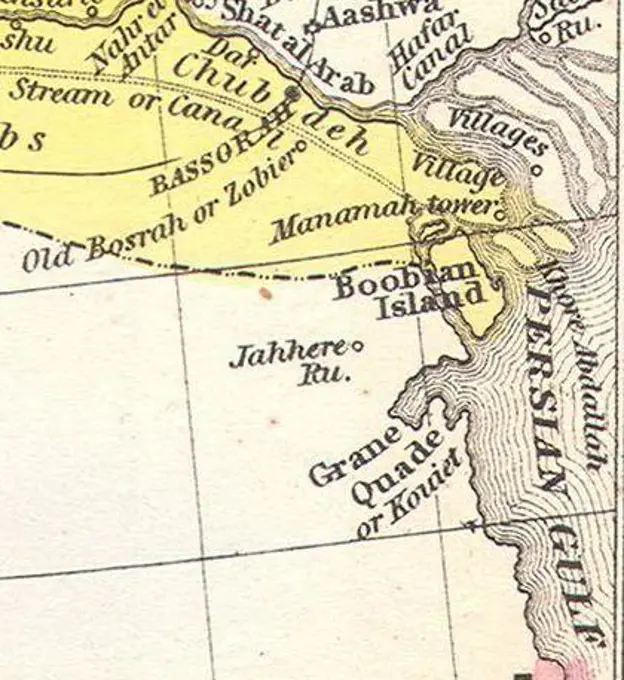
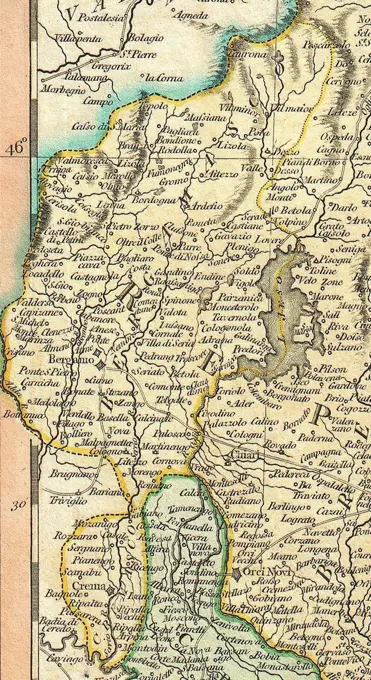
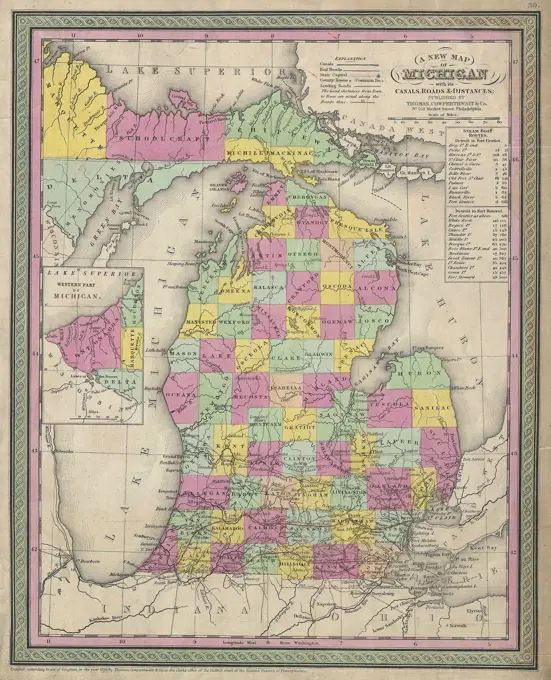
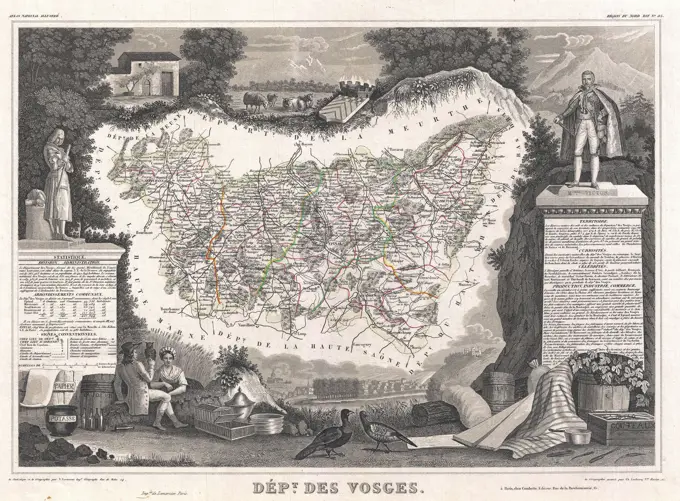
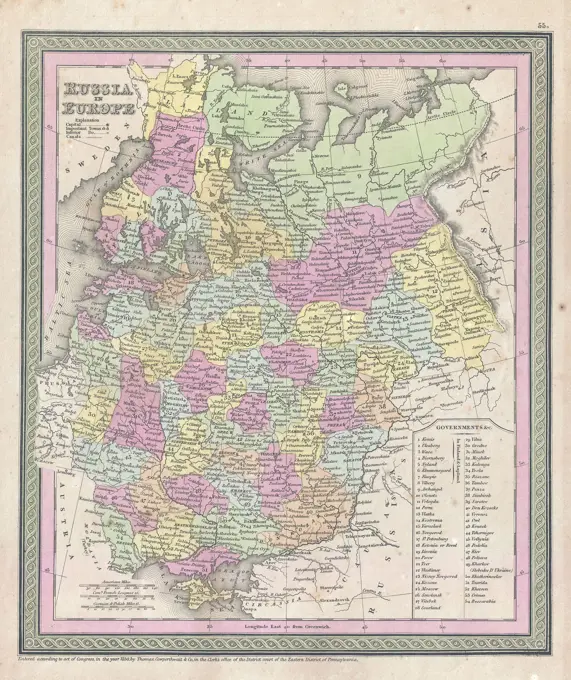
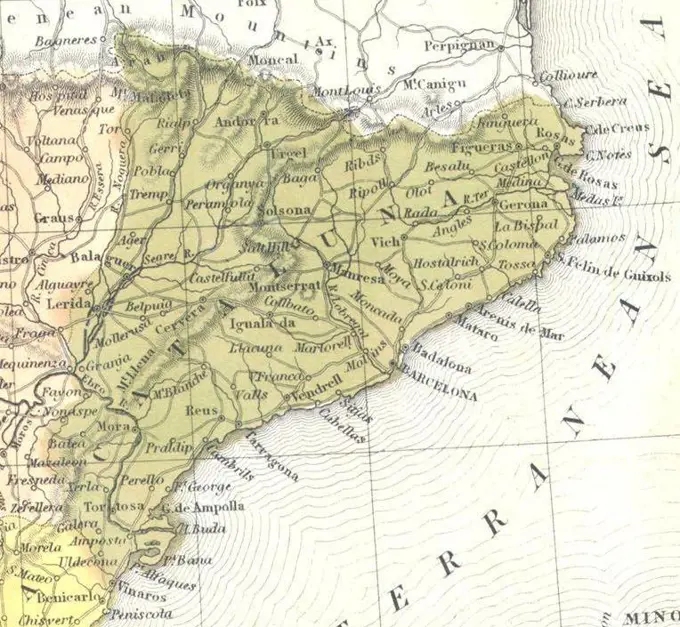
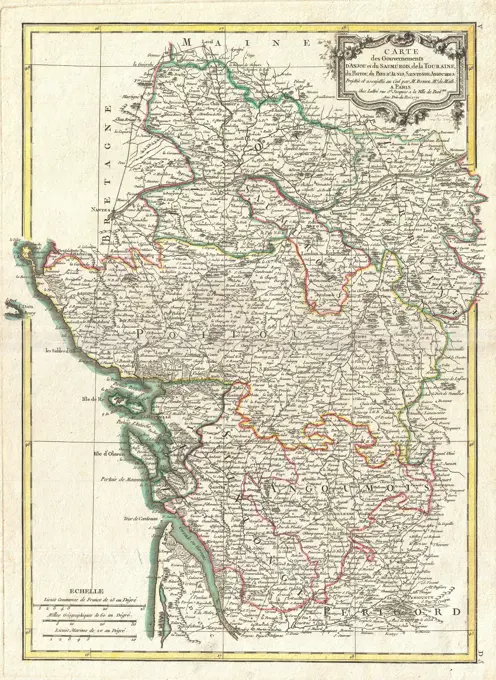
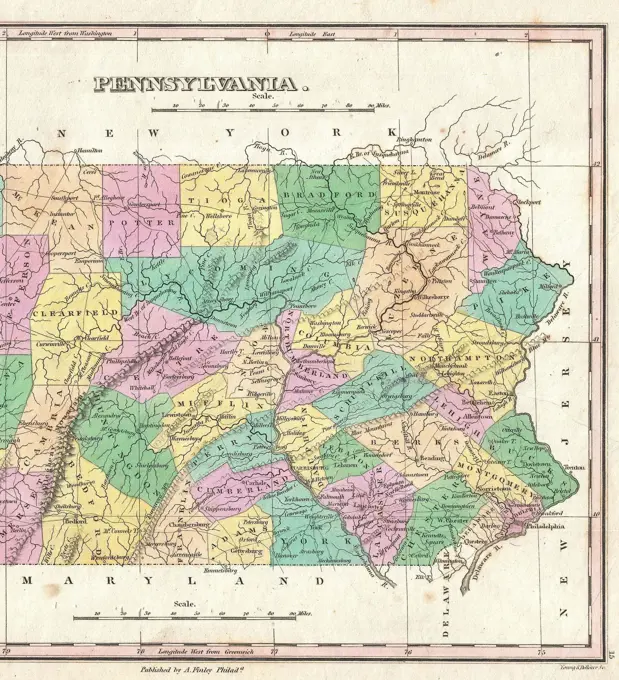
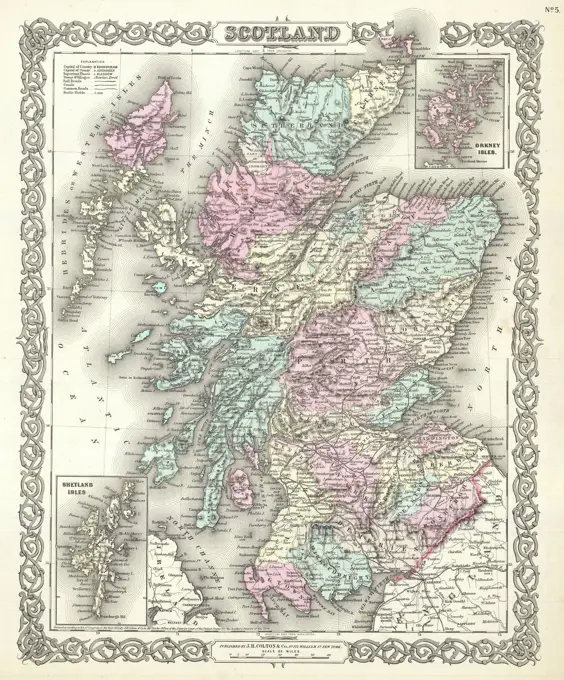
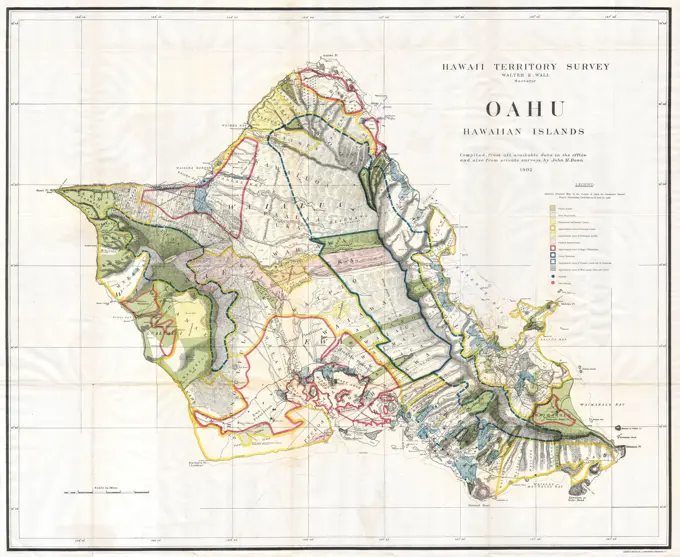
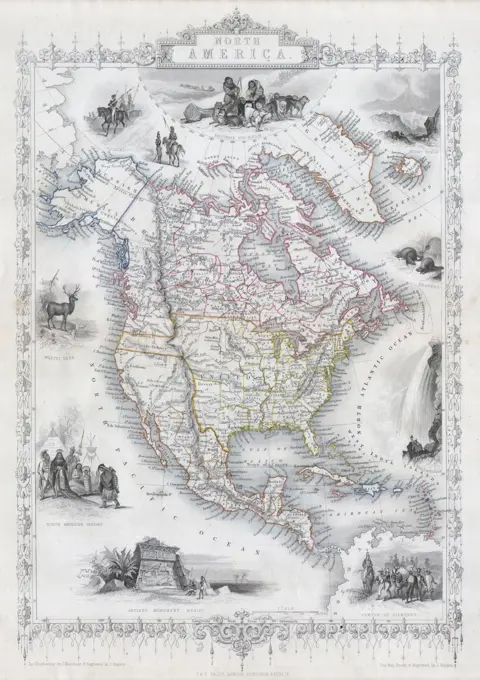
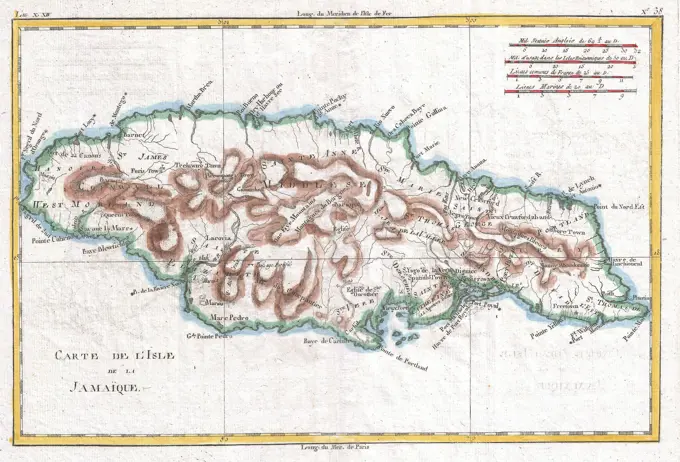
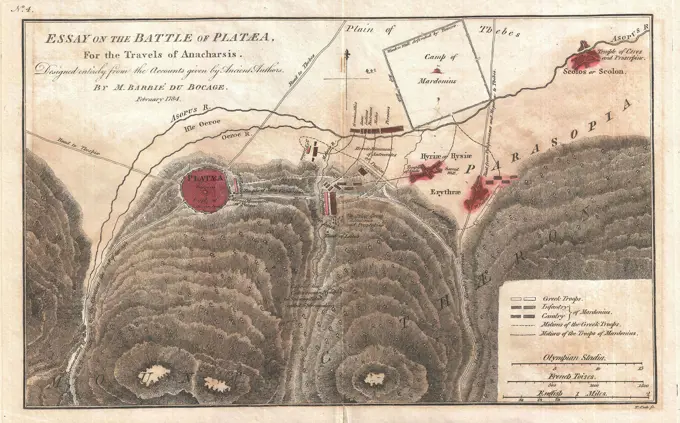
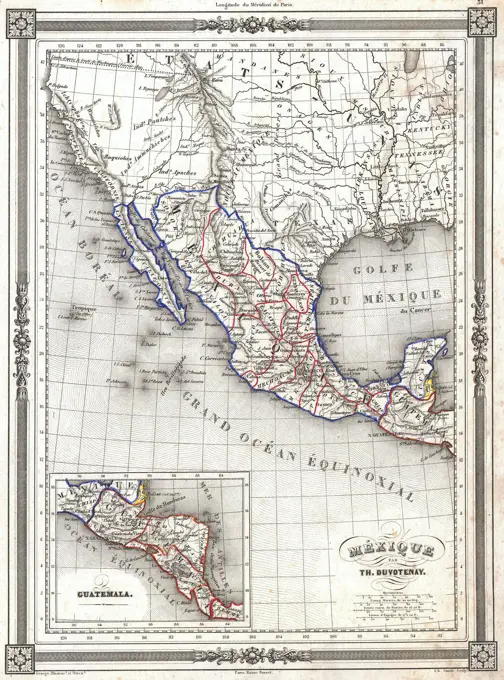
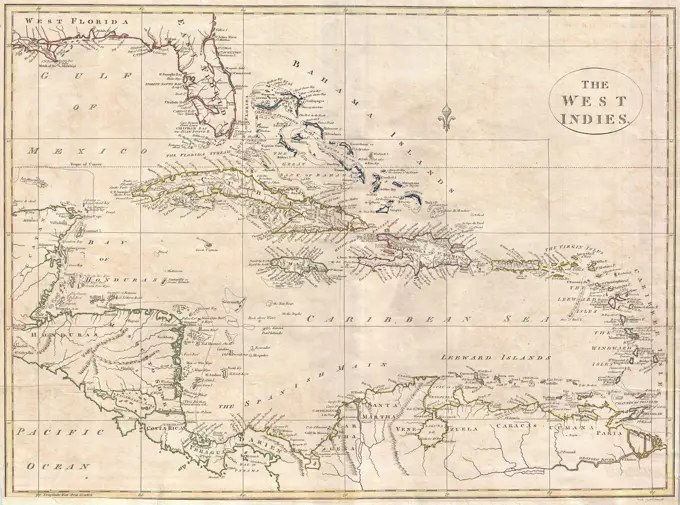
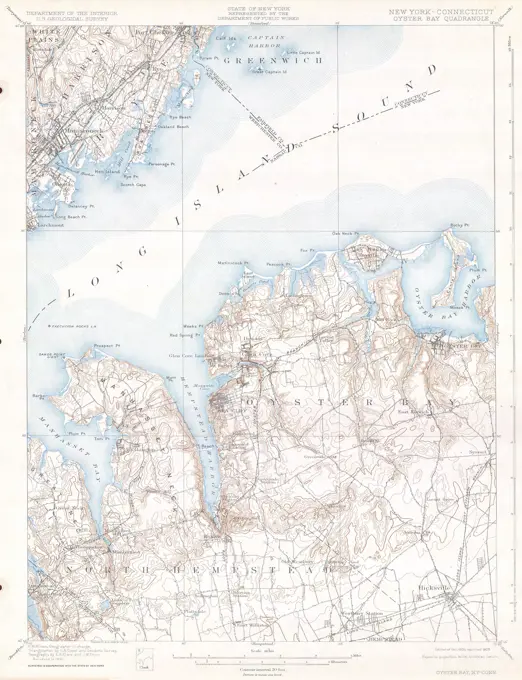
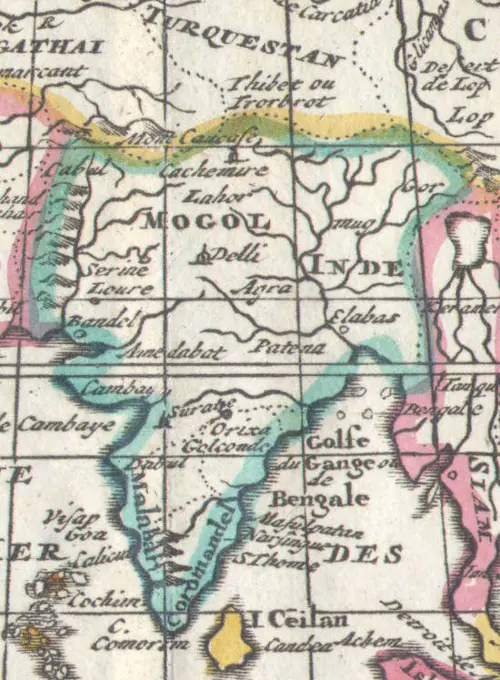
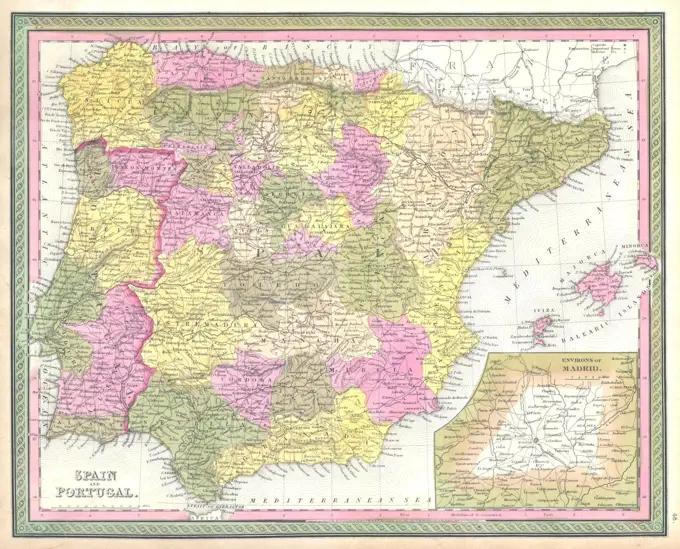
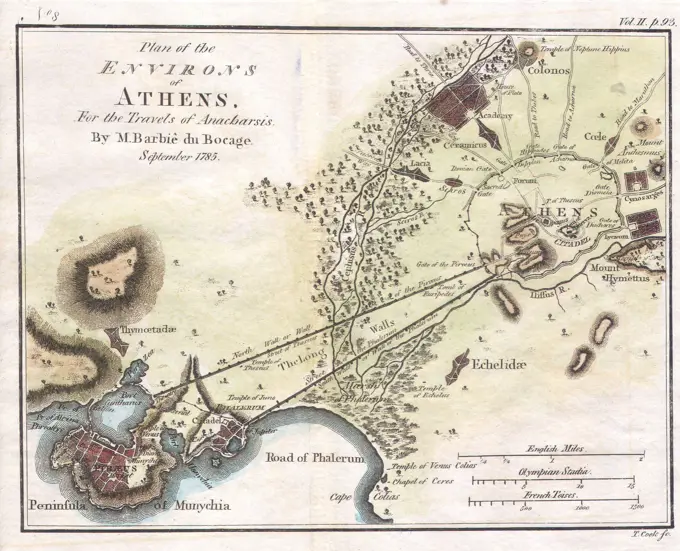
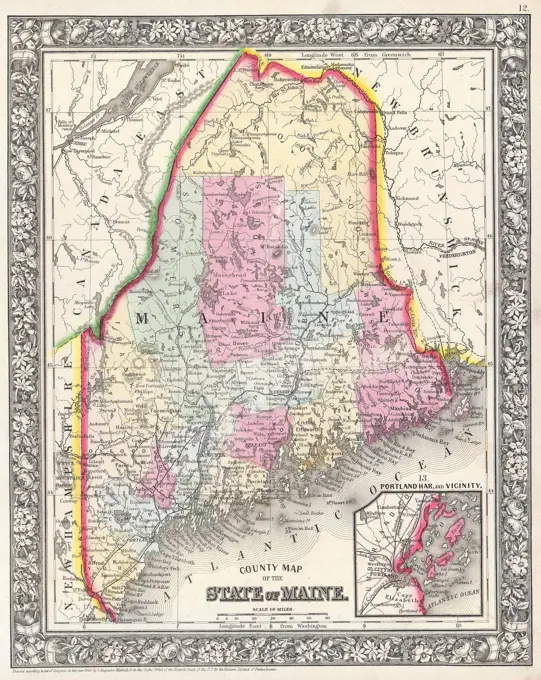
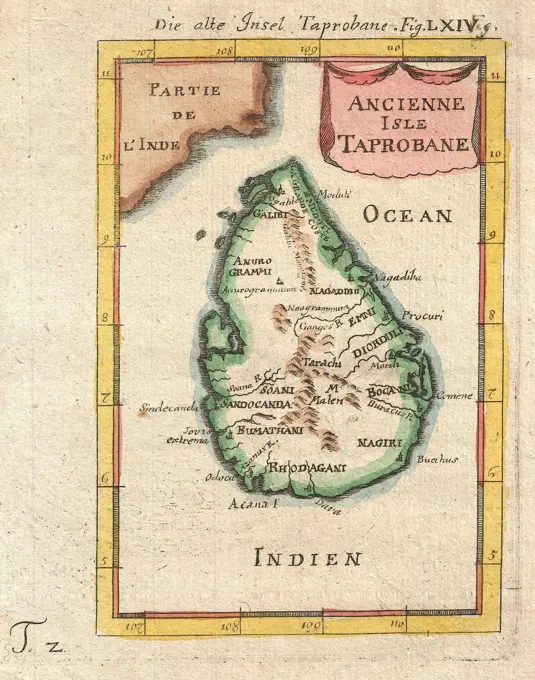
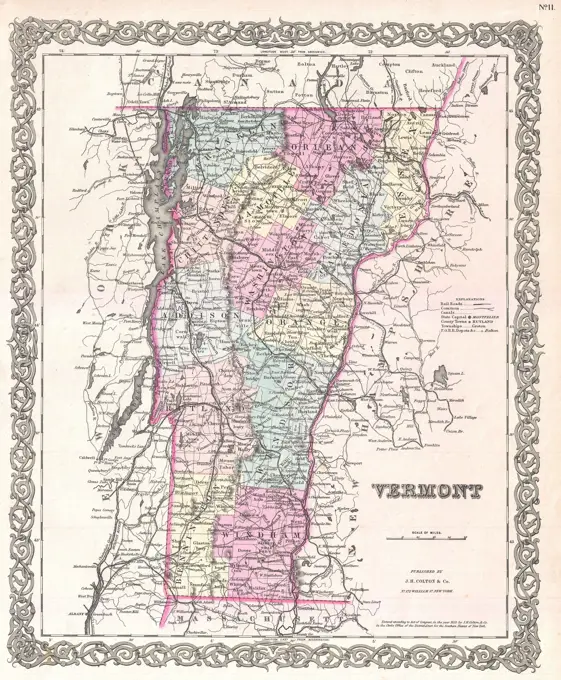
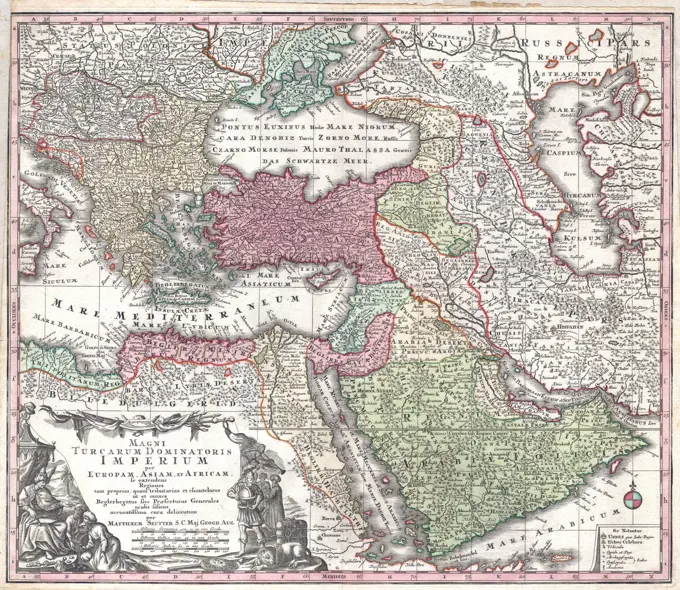
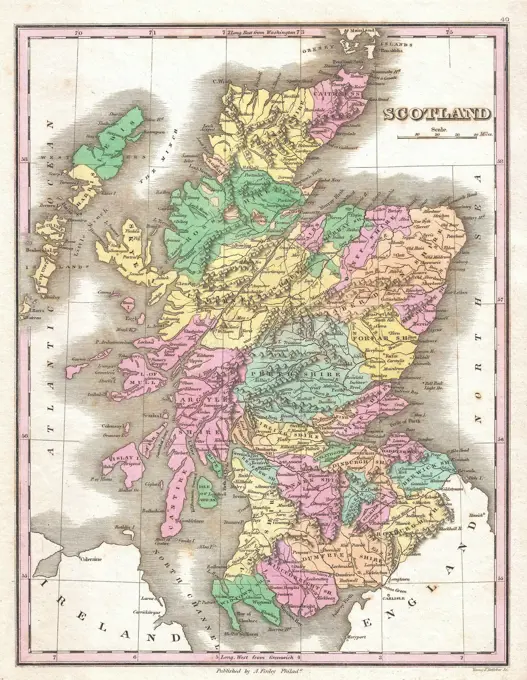
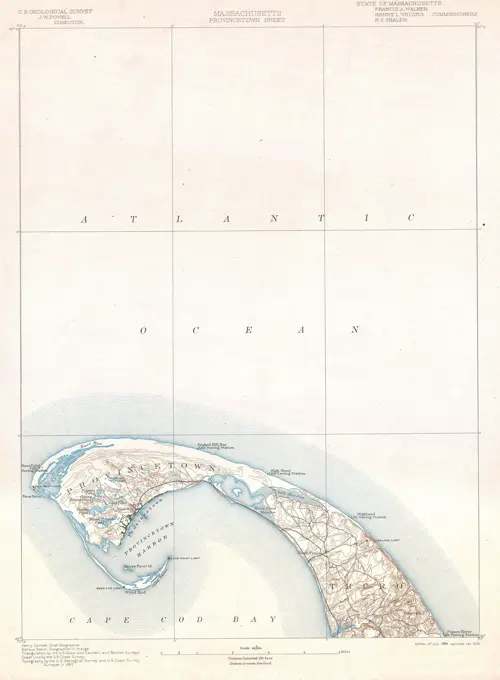
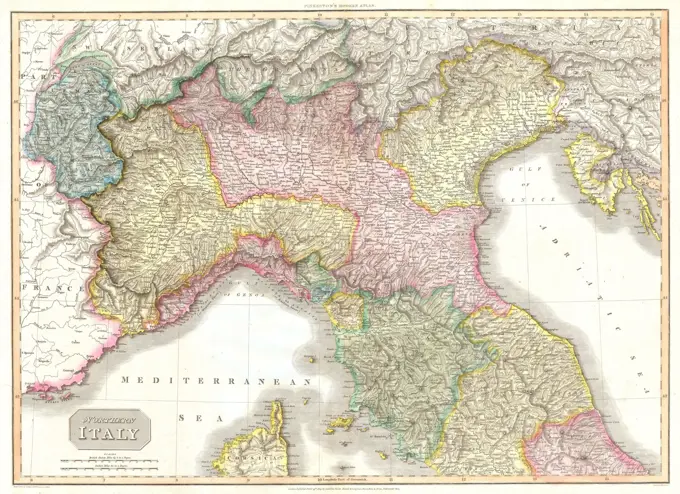
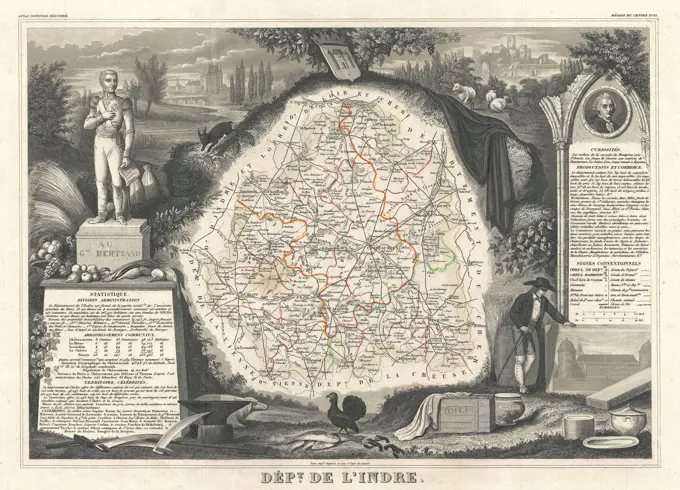
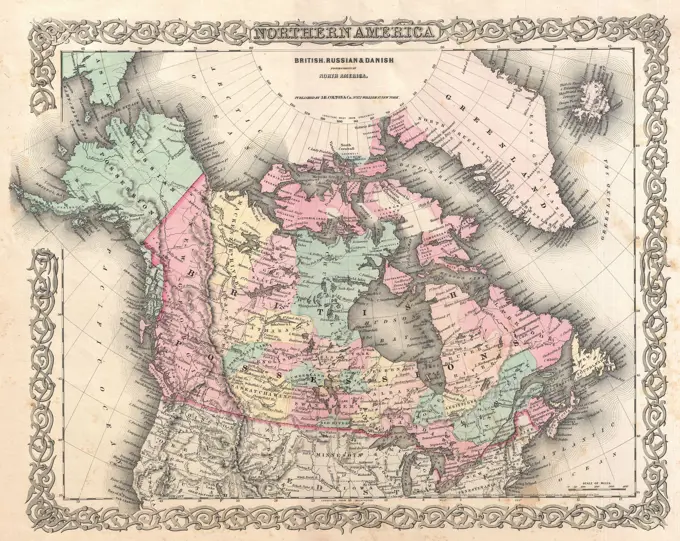
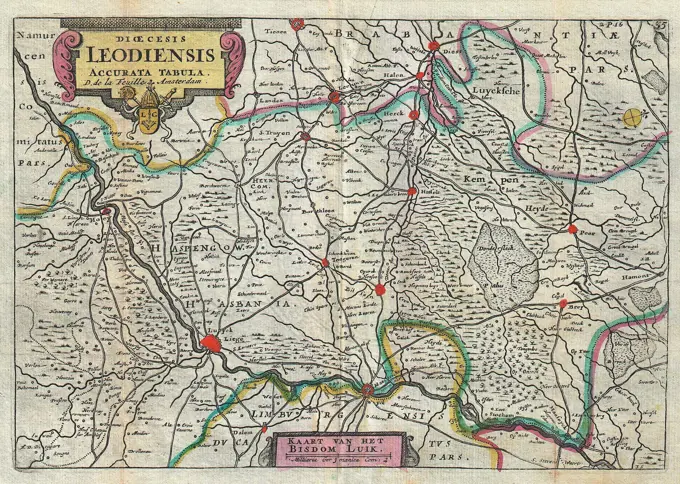
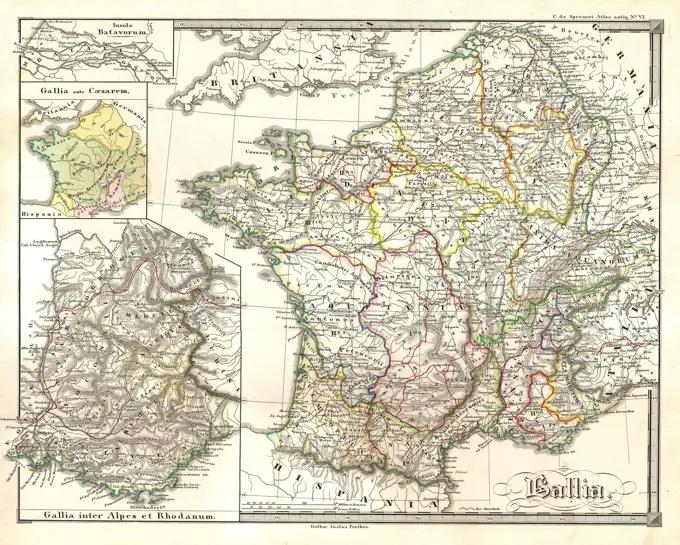
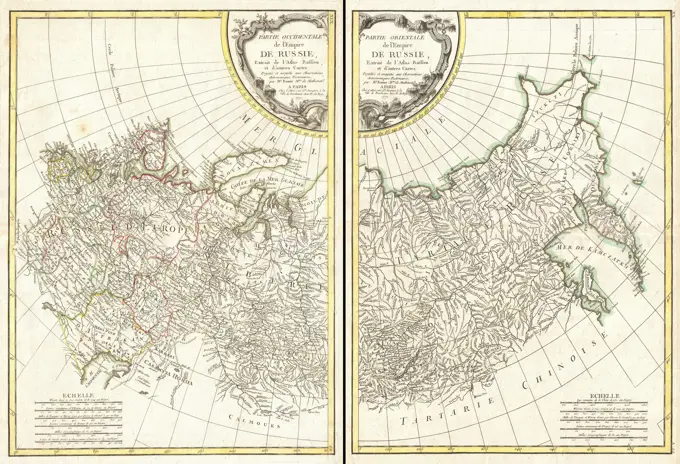
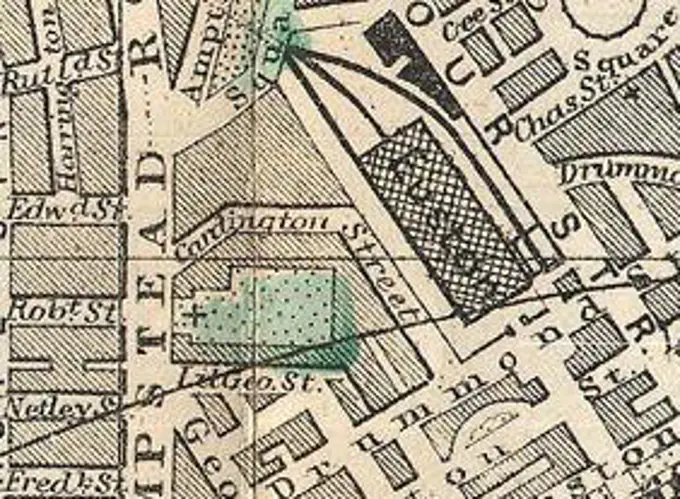
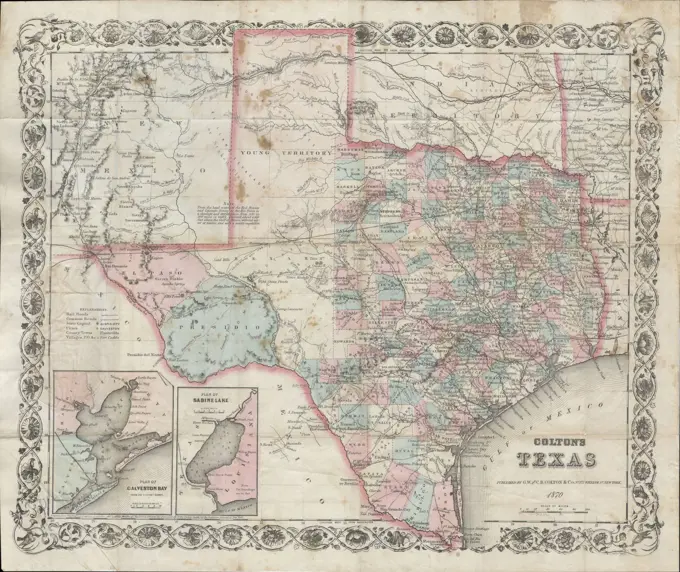
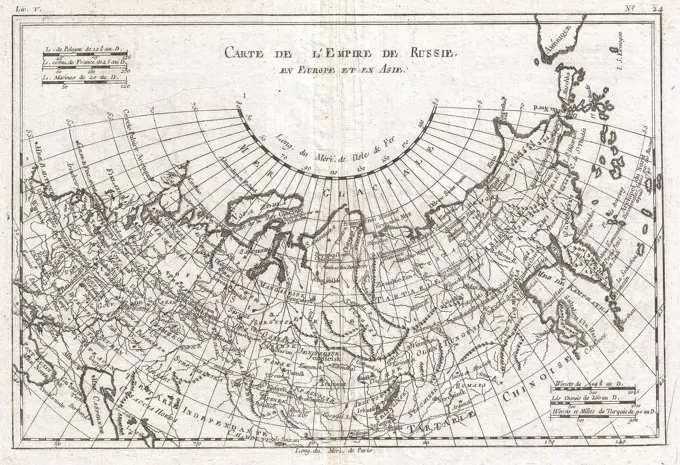
Historical Maps Stock Images
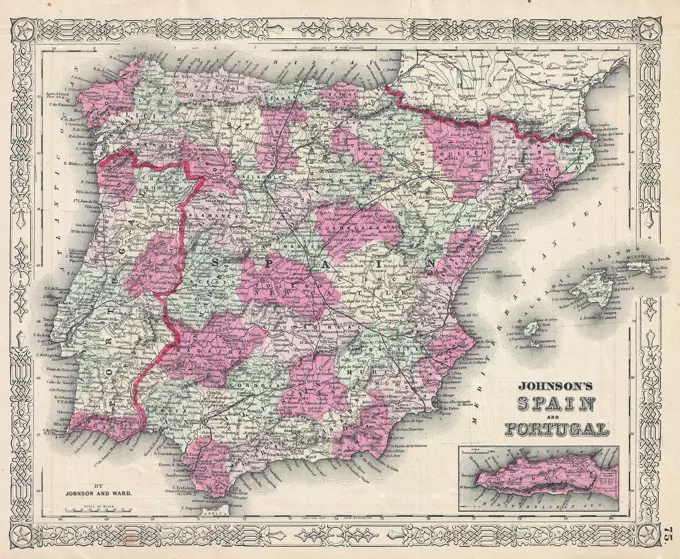
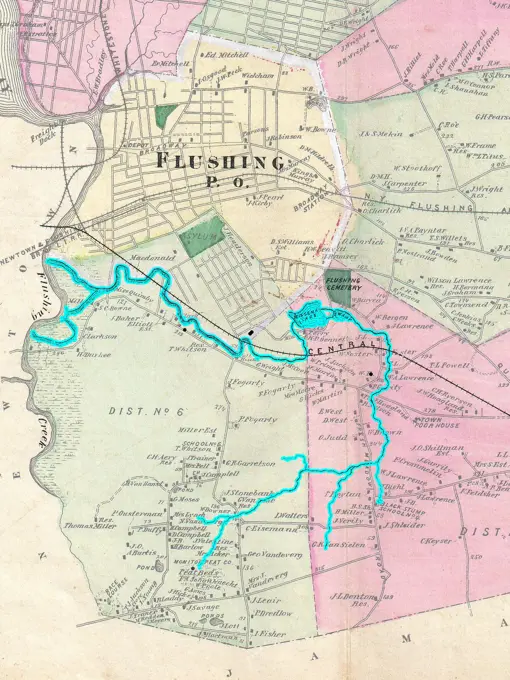
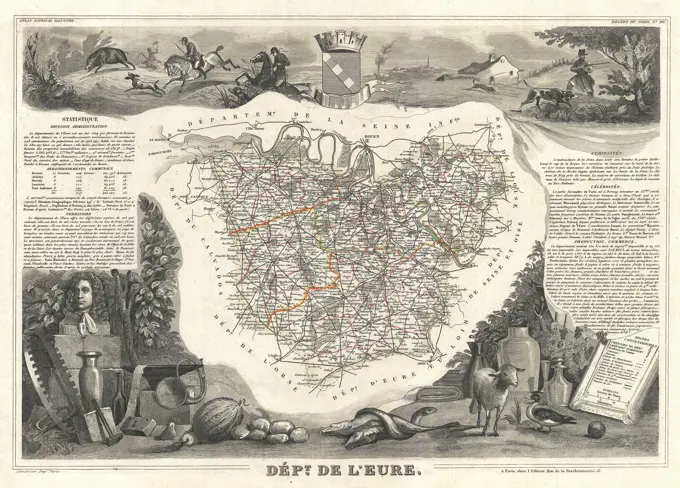
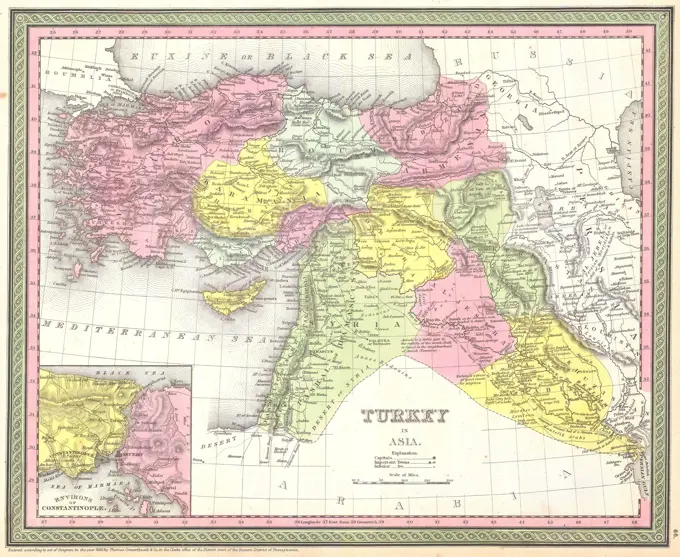
Discover the perfect historical maps stock images for your project at SuperStock. Our collection of high-quality historical maps stock photos offers a unique selection of visuals that you won't find anywhere else. Whether you're looking for a vintage map of a city or an antique map of a country, our gallery has something to suit...Read more